AI has been making waves in virtually every industry, and cyber security is no exception. Several companies are adopting the technology into different business functions, such as logistics and IT.
But as AI quickly leaks into the business landscape, it’s also been the subject of criticism.
Recently, news reports have revealed that ¾ of global businesses are considering or have already implemented a ban on using ChatGPT and other AI applications within the workplace.
This decision is owing to recognized risks they pose on cyber security and data privacy.
In this article, we’ll take a closer look at the benefits and drawbacks of AI and what it means for your business.
The Benefits of AI in Cyber Security
AI has become a powerful tool in the fight against cyber threats as it can help detect, analyze, and respond to malicious attacks faster.
Some benefits of AI in cybersecurity. Image source: OrangeMantra.com
Faster Threat Detection and Response
Leveraging AI helps you better understand your networks and identify potential threats faster. AI-powered solutions can sift through vast amounts of data to identify abnormal behavior and detect malicious activity, such as a new zero-day attack.
AI can also automate many security processes, such as patch management, making staying on top of your cyber security needs easier.
It can help you respond faster to attacks by automating specific tasks, such as rerouting traffic away from a vulnerable server or alerting your IT team to potential issues.
Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
AI-based cyber security systems provide improved accuracy and efficiency compared to traditional security solutions. For example, AI can scan scads of devices for potential vulnerabilities in a fraction of the time it would take human operators to do the same task.
Furthermore, AI algorithms can recognize patterns that may be difficult for the human eye to spot, leading to more accurate detection of malicious activity.
Greater Scalability and Cost Savings
AI can automate tedious security tasks, freeing valuable resources to focus on other business areas.
It can also process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately to identify threats faster than any human could. This helps reduce response times to security incidents and helps lower the cost of defending against cyber threats.
AI-driven tools can also help identify malicious activity by correlating different data points, allowing you to protect your systems proactively. These solutions are easily scalable, meaning you can obtain additional protection without significant hardware or personnel costs.
The Risks of Relying on AI in Cyber Security
AI's ability to analyze large data sets with lightning speed promises unparalleled protection against cyber attacks, and companies worldwide are investing heavily in its application.
But even as AI is increasingly relied upon to bolster security, there are still risks in relying on this technology. 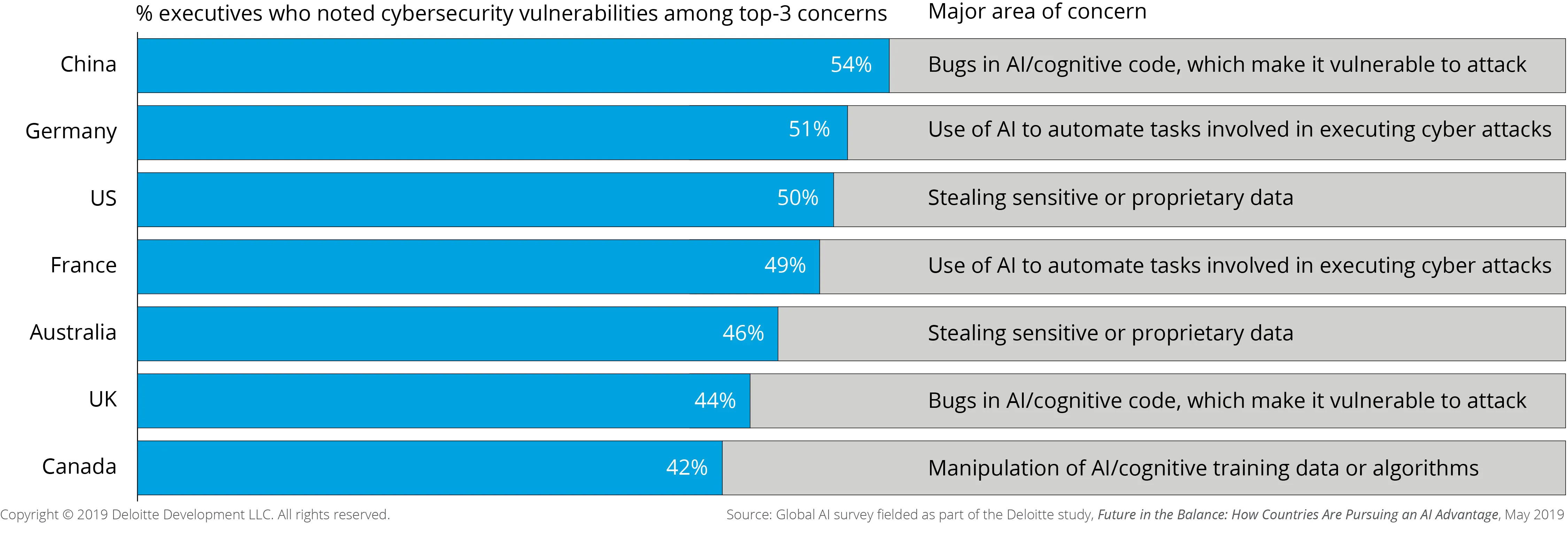
“Cybersecurity vulnerabilities” tops the list of concerns about various types of AI risks in a study by Deloitte.
Bias and Discrimination in Decision-Making
Biased decision-making in AI systems can arise from various sources, including data sets containing biased information or algorithms that lack the necessary objectivity.
If not managed properly, these biases can lead to discriminatory decisions against certain groups or individuals and have significant consequences for the organization.
For example, a decision made by an AI system based on biased inputs could lead to false positives and block legitimate users from accessing company systems, resulting in lost productivity or customers.
Lack of Explainability and Transparency
The algorithms used to make decisions about security threats are not always transparent, leaving you vulnerable to potential bias or manipulation. AI can be difficult to interpret, so it’s hard to understand why decisions were made or how they can be improved.
This lack of understanding can lead to poor decisions, which can have severe implications for an organization’s security.
AI-based cyber security solutions may not always accurately identify every threat or potential breach, leading to potential risks going unnoticed and causing further damage.
Potential for Misuse or Abuse
The good guys aren’t the only ones that can benefit from this technology.
AI algorithms can be designed to search through data and detect patterns quickly, making them an attractive target for malicious actors who could use them to access sensitive information or attack infrastructure.
Examples of AI in Cyber Crime
Cyber criminals may use AI to:
- Easily create new malware that can contain new zero-day vulnerabilities or bypass detection.
- Create new, sophisticated, original, or targeted phishing attacks. Such actions can increase the number of scenarios, making it difficult for reputation engines to keep up.
- Analyze and collect data much quicker and help identify other avenues of attack.
- Create deepfakes (video or audio) that can be used to convince victims in social engineering attacks.
- Conduct attacks such as intrusions or generate new hacking tools.
And because AI relies on data sets that are often biased or incomplete, it can lead to missed threats and false positives, creating a false sense of security and leading to real-world consequences.
Security Concerns That are Driving AI Bans Among Businesses
Research by BlackBerry revealed that 75% of organizations worldwide support bans on ChatGPT and other generative AI applications in the workplace.
Many of these businesses are considering making the ban soon, while some have already implemented it.
IOTs, CSOs, CIOs, CEOs, legal, finance, and HR departments have pushed for the ban, citing concerns that AI apps are unsecured and pose cyber security threats to the corporate IT environment.
Specifically, the security concerns driving bans on ChatGPT and other AI apps include:
- Data security
- Privacy concerns
Companies fear that data storage of these AI systems on external servers could potentially be leaked publicly, posing a security risk for the organization and its clients.
Samsung is among the first to ban its employees from using AI tools. This policy comes after an accidental leak of Samsung’s sensitive information to ChatGPT just recently.
Despite this, many companies still recognize the benefits of AI generative applications in the workplace, specifically in areas of increasing efficiency, driving innovation, and enhancing creativity.
Key factors to consider when implementing AI solutions
When implementing AI to facilitate your business processes, there are several key factors that you should take into consideration:
- Data Quality: Make sure to have a clean and well-annotated dataset to train your model.
- Model Selection: Your AI model will depend on the problem you're trying to solve, the amount of data you have, and the desired level of accuracy.
- Hardware: Consider the computational requirements of your AI solution and ensure that you have the necessary hardware resources to support it.
- Explainability: As the AI model becomes more complex, it's harder to understand how it arrived at certain decisions. It's vital to consider the explainability of the model, especially in sensitive fields like healthcare or finance.
- Security and Privacy: Make sure to consider the security and privacy of the data used to train and deploy the model and the security of the system itself.
- Scalability: Consider how your AI solution will scale as the volume of data or the number of users increases.
- Ethical Implications: Consider the ethical implications of your AI solution, such as bias and fairness.
- Integration: Consider how your AI solution will integrate with existing systems and processes.
- Maintenance: AI systems require regular maintenance and updates, so consider how you will keep your system updated and running smoothly over time.
- Monitoring: Consider how you will monitor the performance of your AI solution and how you will troubleshoot and fix issues if they arise.
Combine AI with the Human Factor
Staying ahead of cyber security threats can seem daunting. With the ever-evolving nature of data breaches, organizations must understand that only one approach is no longer enough. Combining AI with the human factor is key to staying secure and compliant in a digital world.
Before implementing AI into your business processes, ensure that your employees are well-equipped to handle its intricacies and take advantage of its features without posing cyber security risks to your organization.
You can do this with relevant, engaging, and effective security awareness training
Get a free copy of the Definitive Guide to Security Awareness Training to craft a successful program for your employees.