Even after years of business evolution; it’s shocking that safe, quick and trackable payments are still often such a struggle for many companies around the world. Banks are often slow-moving institutions that are late to embrace technological improvements, and currencies have been increasingly fickle in recent years.
This situation is what allowed cryptocurrency to go from the pipe dream of an anarchist hacker to a mainstream concept understood by the general population and used by businesses daily. Many people own Bitcoin and Ethereum as investments, and over 15,000 businesses worldwide accept bitcoin as a payment method.
Source: Buy Bitcoin Worldwide
As with any new evolving technology, there are risks tied to businesses transacting with cryptocurrency, and most of them have to do with cyber security. This means that even if you aren’t actively accepting these currencies as payment, you might still be at risk via a third party.
This guide aims to explain the pros and cons of businesses using cryptocurrency and the associated cyber security risks. Additionally, it will identify the specific ways hackers and scammers use cryptocurrency and a detailed incident response plan and best practices to protect your business.
Pros and Cons of Crypto Payments in Businesses
Types Of Cryptocurrency Scams That Affect Cyber Security
Crypto-specific Cyber Security Threats
Third-party Risk Management and Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrency Incident Response Planning
What is Cryptocurrency?
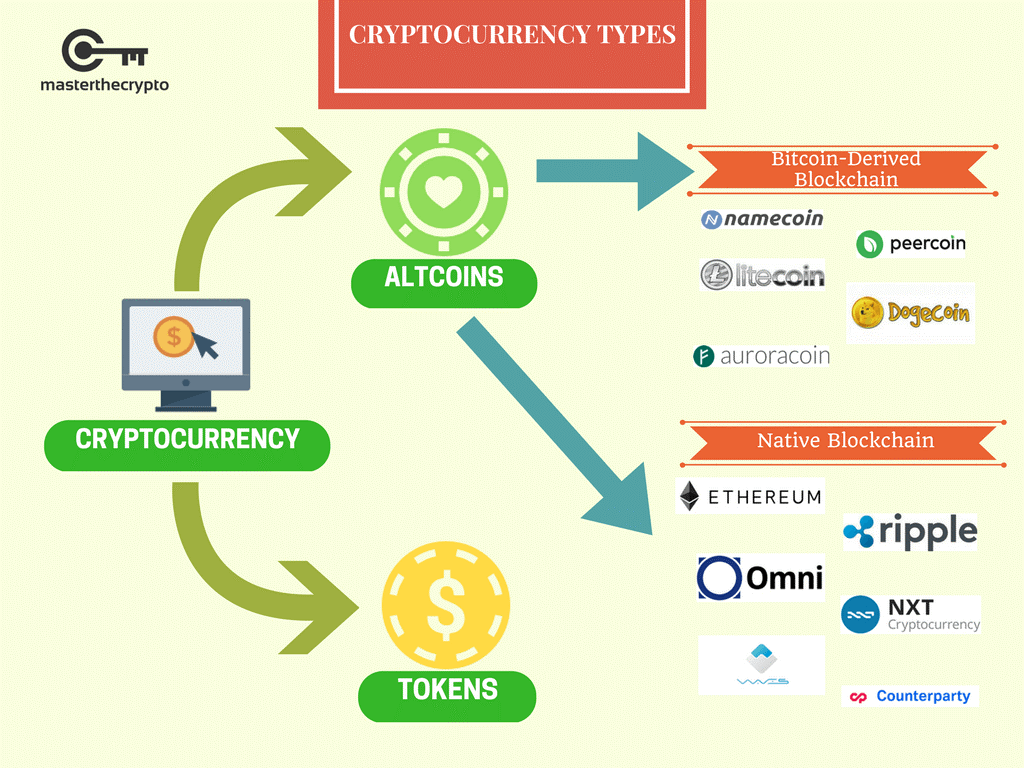
Source: Master the Crypto
Cryptocurrency is a digital or virtual currency relying on cryptography and complete decentralization as security measures. It operates independently from any country or bank and often even from its creators. All transactions and proof of ownership are distributed across a blockchain digital ledger.
Despite their reputation for anonymity, cryptocurrencies can also provide more tracking information than typical transactions if used properly. Since the transaction is recorded at several points on the blockchain, it is relatively simple to monitor a transaction.
Cryptocurrencies can sometimes serve as a store of value or speculative investment, but they are essentially only a different type of payment processing for businesses. Since they are free from country or institutional supervision, cryptocurrencies often have no fees or very small ones to offset the computing costs for any kind of transfer.
Pros and Cons of Crypto Payments in Businesses
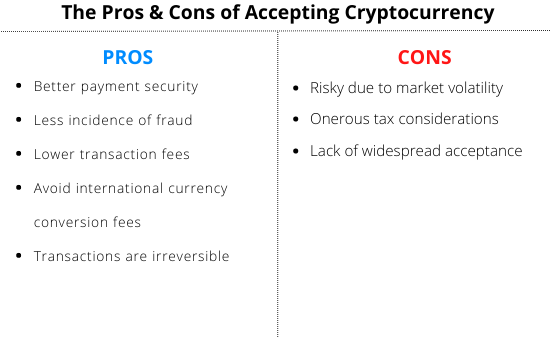
Source: Hello Skip
Crypto adoption in businesses has definitely been timid at best worldwide. A mix of legislative grey area and security issues has resulted in an atmosphere that makes companies reluctant to commit to cryptocurrencies despite their amazing benefits.
Ironically, every pro and con for crypto is almost mirrored, showing that once the cons are ironed out, these currencies will experience an incredible boom.
Lower transaction costs
For businesses that often need to make several large international transactions, the fees charged by traditional banks can easily add up. In some cases, transaction fees can even be a percentage of the amount being sent.
With cryptocurrency, the fees are either nonexistent or very nominal. Unlike banks that charge fees for profit, these fees are only to compensate for the computing power used to make the transaction happen. This keeps fees are a much lower level than typical bank payments.
Faster transactions
For large transactions, traditional banks can require several days of processing, and numerous forms, often only available to be filled in person. While cryptocurrency transactions often still take several hours, the process is much quicker and entirely done online.
Accessibility
In recent years, a number of developing countries have dealt with crippling inflation and dramatic swings in their currency. This has made it difficult for companies located outside of these countries to transact with the affected businesses. If a currency is extremely devalued, everyone ends up getting a bad deal.
Despite cryptocurrencies also experiencing fairly important price swings, more stables like Bitcoin and Ethereum have fared much better than many official currencies. This has been a lifesaver for residents of certain affected countries and has allowed them to export their resources at a fair price.
Volatility
Just like traditional currencies, their crypto counterparts are subject to the fickleness of the market and other economic factors. However, since there is no government overseeing these currencies, if one of them drops, there is no external method to prop it up.
Additionally, certain lesser-known coins are simply scams with no intrinsic value. It’s safer to stick with a well-known cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin or XRP. They are relatively stable and have more robust security built into them.
Regulatory uncertainty
Very few governments have kept up with crypto, which is perhaps the biggest reason companies are reluctant to make the jump. If your country of origin doesn’t have robust legislation around crypto transactions and their tax implications, allocating too much of your revenue to crypto can be dangerous.
In some cases, taxes tied to the gains on cryptocurrencies can end up costing more than their return and make them a net negative on your balance sheet.
Technical complexity
While new platforms making this process easier seem to pop up daily, accepting cryptocurrency payments can still be tedious. For less technologically inclined users, crypto can be a daunting process.
Between understanding new platforms, learning Bitcoin keys and remembering all the new security measures tied to crypto, some businesses will simply be better served by traditional payments for the time being.
Types Of Cryptocurrency Scams That Affect Cyber Security

Source: Cardano
As in any new technology field, scammers have identified crypto to potentially cheat users out of their money. These scams mostly come in two versions:
Investment scams
This type of scam revolves around websites posing as investment platforms with fake charts that make users believe their initial cryptocurrency investment is growing. However, there was never any growth, and by the time users realize they’ve been duped, their money is long gone.
Pump and dump schemes
These scams can have a devastating effect, whether through an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) or via an existing coin. Scammers build convincing websites, marketing materials, and even security whitepapers to present a bogus cryptocurrency as a solid investment.
As they convince more and more people to buy in, the price of the token increases. However, the scammers own the large majority of the tokens, and when the price hits a certain number, they sell all their tokens for traditional currency, making the price crash and leaving the victims with worthless cryptocurrency.
Crypto-specific Cyber Security Threats
Thankfully, most of the cyber security threats linked to cryptocurrency are variations of existing threats applied to a new world. Here is a list of the most common ones:
Fake coins and assets
Online wallets, exchanges and trading platforms pop up every day for crypto, and most of these services are free and easy to create as these companies aim for the highest level of user adoption possible. This has led to a slew of fake coins, especially fake NFTs, being created and “gifted” to unsuspecting companies and users.
The victim then gets a notification that a wallet has been created in their name via email or even that an NFT has been added to their existing wallet by a user. When they download the NFT or add the coin to their cold wallet, malware is activated to either steal other assets or install a keylogger to obtain the passwords linked to the wallet.
Remind your users to delete any coin or NFT added to company wallets without their knowledge. In fact, online wallets are best kept private for most business use to eliminate this risk.
Phishing
Online and cold wallets are the equivalent of bank accounts in the crypto world, making them very attractive targets for hackers. One of the most dangerous aspects of crypto phishing is that transferring funds is as simple as entering a wallet address in a crypto exchange. Since they are usually long alphanumerical strings, it’s easy for users to make a mistake and send funds to the wrong one.
Many services and exchanges offer address validator apps that are much safer than copy-pasting a wallet address directly from an email that might be from a fraudulent source.
Man-in-the-middle attacks
In the case of most well-known cryptocurrencies, the blockchains are very secure, and their decentralized nature makes them virtually impossible to hack. However, with lesser-known cryptocurrencies, blockchains can be infiltrated to intercept transactions and reroute the coins to a different address without the user realizing it.
The same goes for lesser-known exchanges with subpar security measures or that might even be built from the ground up with a backdoor. Hackers can then easily see all the transactions before they happen and swap out their addresses to steal funds.
Related reading: Protect Your Personal Information from Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks
Third-party Risk Management and Cryptocurrency
Even if you don’t use cryptocurrency in your business, you might still be exposed to its threats through a third party who does accept it. Payments are definitely an aspect you want to add to your auditing of technology partners since it can have many cyber security vulnerabilities and devastating effects.
The most common third-party risk management issue in regard to crypto is custodial wallets. When buying or transferring cryptocurrency on an online exchange, funds must transit on a piece of software called a crypto wallet. While many exchanges build their own, several exchanges also white-label another company’s product for their needs.
These wallets are generally safe for a short duration while your funds are transferred to a safer cold wallet. However, it’s important to keep in mind, and to add this question to your cyber security checklist. You might feel confident in the exchange’s measures, but if they use a third-party wallet, this adds another potential failure point in your payment supply chain.
Cryptocurrency Incident Response Planning
The steps of incident response planning are the same as any cyber security threat when dealing with cryptocurrency. Make sure you look at all the threats previously listed and identify where there might be related vulnerabilities in your accounting department.
Make sure that all transactions done in crypto are monitored and carefully double-checked to ensure the funds are being sent to the right destination. This will save you precious time in the analysis phase once a threat is detected.
The containment and eradication phases are only useful in the event of malware and fake NFT assets and can easily be removed from the list by using private accounts exclusively. The recovery phase is also sadly often removed from the equation in crypto. Once funds are sent to the wrong address, many “tumblers“ services like TornadoCash allow hackers to anonymize funds by splitting them into hundreds of accounts.
The most important step, as always, is to run a thorough post-incident report to understand your company’s vulnerabilities in regard to crypto payments. In this world, the best protection is definitely prevention since there are no banks or overarching entities to rely on in case of theft.
How to Avoid Cryptocurrency Scams

Source: Currency.com
While there are still several risks to using cryptocurrency in your business, they aren’t any worse than the ones already present with normal currencies as long as you have security measures in place. Remember that, unlike traditional money, your users have to act like they are the bank.
In a way, cryptocurrency is safer since it has much fewer transfer points for the money, meaning there are far less opportunities for vulnerabilities. The real issue lies with the proper securing of the funds once they reach your accounts.
Use cold storage wallets
It’s been proven time and time again with exchanges, big or small, if your crypto isn’t in a cold wallet, it’s not really “yours”. Of course, you still need to use exchanges to make transactions, and most of the established ones, like Coinbase are relatively safe.
However, as soon as a transaction is done, all funds should be transferred to a cold wallet. These small hardware devices are essentially hard drives that can’t connect to the internet where you house your cryptocurrency keys.
Since they never connect to the internet, they can’t be hacked. In the event of a major hack of an exchange or if it becomes insolvent, you still have access to your funds via the keys stored in your cold wallet.
Maintain a good password hygiene
Like any other device storing information, cold wallets are governed by a password and 2FA authentication. Good password hygiene is especially important in this situation since it potentially controls large sums of money.
Make sure that your organization uses a recognized password manager to house your passwords and crypto keys. Additionally, turn on 2FA authentication, ideally connected to an authenticator app instead of text message authentication.
Encrypt your keys
While cold wallets can’t be hacked remotely, they can still be broken into if a criminal gains physical access to them. For this reason, investing in a high-quality cold wallet that encrypts your keys is critical, making them that much harder or virtually impossible to break.
For the same reason, it’s also a good idea to have backups of your cold wallet information and keys in case of theft.
Train your users on crypto
Like in most cyber security scenarios, this all comes down to user training and cyber security awareness. It’s especially important in this scenario because users who handle cryptocurrency for your business lose some of the built-in failsafe when dealing with a bank.
Cryptocurrency accounts aren’t as inherently safe as banks since they are largely unregulated. This means their security level depends entirely on what the exchanges deem necessary, with varying levels of success.
Make sure they understand the subtle differences in crypto cyber security and train them to identify phishing attacks and malware signs in this world.
Protecting Yourself from Cryptocurrency Scams
Cryptocurrency’s time to shine is now. The level of international adoption, security measures and relative recent price stability has started to outweigh and eliminate many of the cons that prevented certain businesses from accepting it as payment.
Perhaps the biggest rule is picking one or two stable cryptocurrencies you exclusively transact in. Make sure you are comfortable with their recent price fluctuations and pick one with a solid blockchain and wide user adoption, like Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin or XRP.
Then, put in place a dedicated process to ensure funds spend as little time as possible on online exchanges and accounts, even on reputable ones. Your crypto is at risk as long as your funds aren’t safely stored within a password and 2FA-protected cold wallet.
![]()
Cyber Security Hub: Access Exclusive Cyber Security Content
For more tips on building a cyber aware culture in your organization, visit our CyberHub.