Foreword
As the cyber threat landscape continues to change and evolve rapidly, so has security awareness training. Attacks that leverage phishing, ransomware, malware, and many other techniques have put cyber security under an even brighter spotlight for organizations worldwide.
As a result, conservations around securing sensitive information have shifted beyond meeting minimum internal, industry, or regulatory awareness training requirements. It’s become a discussion about making cyber security awareness not just a priority but an integral part of an organization’s cultural fabric.
Whether your employees work in-office or remotely, communicating the importance of safeguarding data from cyber criminals is critical. In many cases, phishing simulation benchmarking statistics serve as an essential starting point, enabling security leaders to establish existing behavior trends and craft strategies to help reduce risk and strengthen information security.
Microsoft was proud to co-sponsor the 2022 Gone Phishing Tournament and work with Fortra’s Terranova Security on the phishing template used during the event. The goal was to deliver a phishing scenario relevant to employees’ day-to-day while also drawing on real-time Microsoft phishing email data to deliver the latest trends in phishing attack scenarios.
Microsoft is thankful to count on Terranova Security as our global security awareness partner of choice. Together, we’re committed to bringing the industry’s best phishing simulation training to customers everywhere and fueling the growth of security-aware organizational cultures.

Security Awareness Training: Doing it for the Culture
Cyber security awareness is having a moment
With cyber threats growing more complex and ubiquitous with each passing day, understanding how to detect and handle them is vital to an organization’s productivity and profitability. However, even with security awareness training programs in place worldwide, employees still click on malicious links, download suspicious attachments, or otherwise compromise sensitive information.
Why?
The answer involves shifting mindsets at the cultural level. Gone are the days when simply deploying cyber security training courses would provide employees with the support they need to safeguard data and systems. The most crucial metric for awareness training success is whether it can foster a security-aware approach to all employees’ daily activities.
The 2022 Cyber Culture Report, created in collaboration with research firm Ipsos, revealed many organizations have a long way to go to attain this level of awareness. In the United States alone, 35% of employees express little concern about work-related data theft, while 76% believe it’s the IT department’s job to protect organizational information.
Despite those shortcomings, employees are still the first line of defense against many cyber attacks. More importantly, they have an appetite for learning and growing, which is where real-world phishing simulations come in. By allowing everyone to learn how to spot cyber threat warning signs in a safe, hands-on environment, security leaders can put all employees in a position to become cyber heroes.
What is the Gone Phishing Tournament™?
The Gone Phishing Tournament (GPT) is a free annual cyber security event that empowers organizations globally to strengthen their security awareness training programs with in-depth benchmarking data. The insights generated by this data help security and risk management leaders better understand their organization’s phishing vulnerabilities compared to their peers, establish concrete cyber security goals, and maximize their return on investment.
The 2022 edition of the event once again benefited from the partnership between Terranova Security and Microsoft. The two organizations collaborated on the phishing template used for the phishing simulation, leveraging real-world Microsoft intel to portray the emulated cyber threat accurately
The 2022 Gone Phishing Tournament Methodology
The GPT is open to all security leaders and their organizations annually. The 2022 edition participants included existing Terranova Security customers and parties with no prior relationship with the company.
This global phishing simulation aims to measure and evaluate employee behaviors with realistic phishing threats they may encounter. Instead of gauging performance across various phishing scenarios, like other cyber security awareness phishing and benchmarking reports, GPT leverages the same phishing simulation for the event’s duration.
This consistency means click rates and related actions are based on the same simulated phishing threat. This section offers a detailed breakdown of the 2022 GPT methodology, information on the simulation itself, and an overview of the participants and the global event strategy.
About the simulation template
Microsoft supplied this year’s email and webpage templates. They imitate a real-world scenario that all end users are likely familiar with: a gift card scam. The scenario, selected by the Terranova Security leadership team, measured several end user behaviors, such as clicking on a link in the body of a phishing email and entering credentials into a form on a phishing webpage.

Terranova Security in-house experts rated the template’s difficulty level medium-high for complexity. This rating was based on the number of phishing indicators and how difficult it was to spot various warning signs. The email and webpage spoofed the look of many gift card email offers to ensure an authentic look and feel. The email message promised the gift card would be delivered after the recipient completed a short, one question survey, adding further motivators to click to the mix.
Simulation strategy

The 2022 GPT took place from October 17 to 28. Throughout the process, Terranova Security operated using its existing data security controls on its Security Awareness Platform.
If users clicked on the link in the phishing simulation’s email, they were redirected to a landing page, which prompted them to enter credentials that, had the simulation been a real attack, would have been compromised. If users completed this second step, they were brought to a phishing simulation feedback page highlighting the warning signs they missed and the best practices they should observe in a similar scenario.
After the tournament, Terranova Security began the data analysis stage of the event. All participant data was anonymized, and after the analysis was finalized, all information used during that process was deleted, ensuring end-to-end data privacy and security for participating organizations.
Overall, the success of each hinges on an organization’s ability to obtain an accurate picture of its employees’ click rates and compare them to their peers.
Simulation languages
To provide participating organizations with an inclusive experience, the 2022 GPT template was sent in more languages than in previous years (21 in total), including:
Participating organizations overview
The 2022 GPT was the biggest in Terranova Security history.
Over 250 organizations and 1.2 million users participated in this year’s event, making it one of the largest phishing simulations of its kind. The increased demand to partake in this global phishing simulation highlights how seriously organizations are taking phishing awareness in light of the ever-increasing complexity and prevalence of real-world threats.

Representation by industry
As in previous years, the GPT welcomed participating organizations of all sizes and backgrounds. The event saw Information Technology emerge as the industry with the most participating organizations, followed by Finance, Education, and the Public Sector.
The nature of each organization’s existing security awareness training program also varied considerably based on their sector.
The industries with the highest number of existing programs that included both security awareness courses and phishing simulations, which is the best possible combination, included Energy, Finance, Healthcare, and the Public Sector. Meanwhile, Information Technology and Education were at the other end of the spectrum, with only 37% and 38% of participating organizations utilizing both facets, respectively.
An encouraging sign for security leaders will be the decrease in the number of organizations with no training initiatives implemented. For example, 33% of participating Not For Profit (NPO) organizations reported having no security awareness training program in place. Not ideal, but a sharp decrease from the 60% reported in the 2021 edition of this report.
Only two sectors, Finance and Consumer Products, saw less than 10% of their organizations without a security awareness training program, sitting at 6% and 7%, respectively
Summary of Findings
The 2022 GPT results revealed many end users are still prone to following through on requests for sensitive information, even if they come from unknown or suspicious email senders.

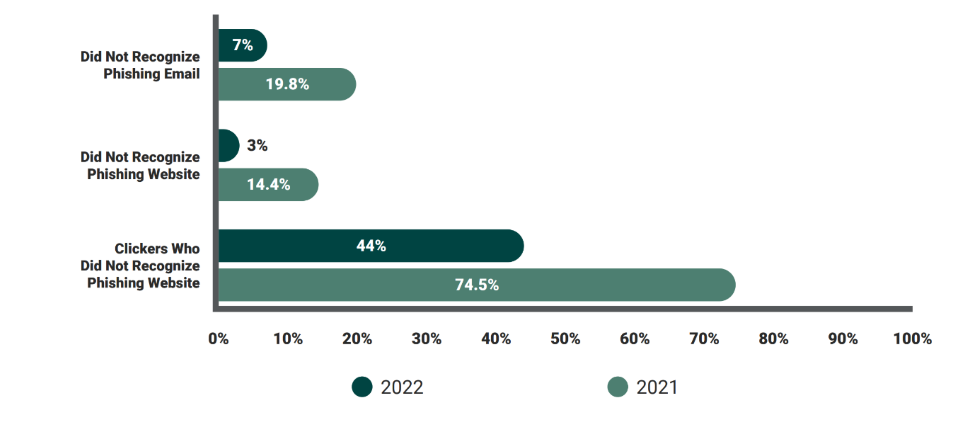
7% of all phishing simulation email recipients clicked the message’s phishing link. This result showcases a marked improvement in click rates from the 2021 and 2020 editions of the event. The latter is particularly insightful since that year’s simulation similarly tested end-user behaviors related to credential harvesting.
Globally, only 3% of all recipients failed to recognize the phishing webpage and submitted their credentials in the form. This statistic is also a significant improvement when stacked against results from 2021 and 2020, where 14.4% and 13.4% of end users, respectively, would’ve completed an action that compromised sensitive information had the simulation been an actual cyber attack.
ALL USERS ACTIONS
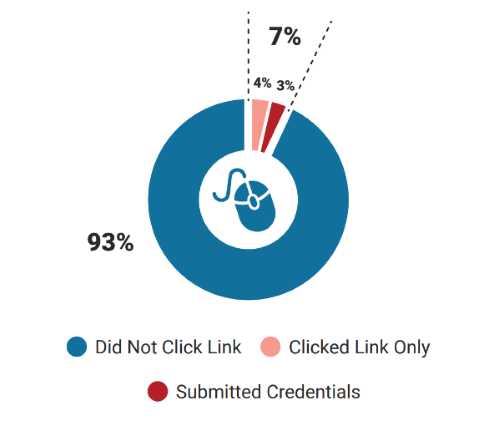
Despite these developments, this year’s click-to-form-completion ratio (CFCR) is still a cause for concern. Globally, of those who clicked on the phishing simulation email link, 44% completed the web form on the subsequent webpage. Arguably more concerning: only organizations with an employee base of 500 or less registered a CFCR under 30%.
These findings underscore why building an engaging security awareness training program that leverages hands-on, practical exercises like phishing simulations is essential. Technical infrastructure like firewalls, endpoint security, and even phishing report buttons in a corporate email client can’t guarantee information security.
It’s up to employees to strengthen their cyber security knowledge levels and bolster an organization’s first and most crucial line of defense against hackers.
ACTIONS ON PHISHING WEBSITE
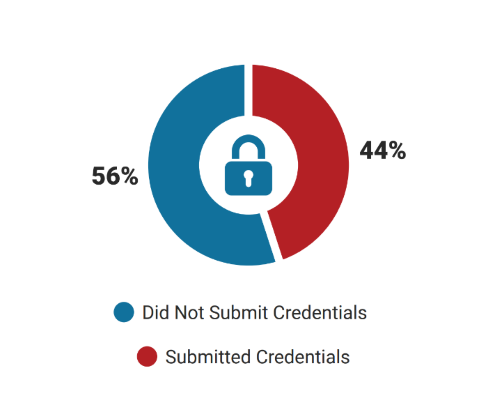
What is CFCR?
Click rates and form completion rates look at what percentage of all participants took action, but it’s not always clear why users did not click. Maybe they never came across or reacted to the phishing email. The CFCR metric measures the action stemming from the decision we know users who clicked faced: submit data on a form or not. The ones who did not submit data were therefore able to identify the phishing webpage.
How Phishing Impacts All Organizations
Successful phishing attacks can inflict financial harm on organizations and their customers, suppliers, and investors. They can also suffer irreparable damage to their reputation through diminished consumer trust in their data protection capabilities.
These consequences can arise from even the most innocuous-seeming emails, like the one referenced in the 2022 GPT simulation. Due to increased reliance on remote work and seismic changes to the average professional’s online habits, accidental data leakage due to unauthorized access to documents or systems can stem from a single compromised online account or password.
The negative impacts can be widespread if an organization doesn’t implement a security awareness training program that includes practical, interactive content like phishing simulations. Heightened risk levels due to human error may discourage investors and external partners from associating with any brand they deem more susceptible to cyber threats. As a result, potential buyers may choose a competing solution.

In their 2021 Internet Crime Report, the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) received over 847,376 phishing-related complaints, with potential losses of over $6.9 billion. Despite this, according to the 2022 Cyber Culture Report, 52% of employees still say their job has nothing to do with cyber security
Couple that reality with a growing number of apps and devices being used daily, and addressing the human risk factor must be a top priority for all organizations, regardless of industry, region, or size.
Phishing Simulations: A Crucial Part of Cyber Security Awareness
To reduce cyber security risk, organizations must first identify their most vulnerable areas or team members.

Who are the high-risk employees? Which roles have the most inherent risk factors, such as access to sensitive information and the volume of emails received? And, most importantly, how is security awareness training performance contributing to overall risk reduction (or a lack thereof)?
With billions of fraudulent emails sent every single day, understanding existing security knowledge levels and potential areas for growth is a critical part of bolstering the human aspect of information security. Even if an organization’s technological guardrails are among the strongest available, employees are still the first line of defense against potential data breaches.
To adequately assess risk, phishing simulations that reflect common cyber threats and how they may target the average end user are a great place to start. This tool enables security leaders to place all team members in a real-world scenario that measures cyber security aptitude through practical actions—whether they clicked on a suspicious link or attachment, and so on.
Leveraging the data-driven insights empower decision-makers to:
Reduce risk levels by a considerable margin
Increase organizational awareness of the latest threats
Minimize the costs associated with being victimized by a phishing attack
Accurately measure individual and organizational vulnerability levels
Lessen the automatic trust response by changing user behavior
Provide employees with targeted training and just-in-time feedback
Improve user reporting and responses to phishing attempts
Assign specific role-based phishing training for enhanced relevancy
Protect confidential data, both personal and organizational
Create a cyber-aware culture made up of proactive cyber heroes
By knowing exactly where the organization stands, security leaders are helping strengthen data protection!
Results
Most of the world’s cyber attacks take advantage of basic human emotions, such as the willingness to trust an offer or individual, to access and compromise sensitive information. If an online account or password falls into the hands of a cyber criminal, confidential data, including personal and financial details, could be left vulnerable to theft or other malicious activity.
Fueled by Microsoft’s real-world phishing email intel, the simulation crafted for the 2022 GPT targeted a typical end user behavior while maintaining an elevated level of complexity. Since only one template was sent to all participants, the insights delivered in this report are among the most universal in the industry.
The following sections will examine overall results and trends before breaking down the event’s data by industry, organization size, and region. The overall and regional findings and breakdowns are based on total end-user click rates to ensure all variables are weighted equally. In contrast, industry and size segment findings are based on click rates per organization.

Overall
In total, 7% of all end users who participated in the 2022 GPT clicked on the link in the phishing email, a significant improvement compared to the 2021 and 2020 event results. In addition, 3% of all end users failed to recognize the warning signs of the simulation’s webpage and proceeded to enter their credentials on the malicious webpage.
Despite those encouraging numbers, the click-to-form-completion ratio (CFCR) was still higher than any CISO would like. Globally, 44% of those who clicked on the phishing email link also entered their information into the form on the simulation’s webpage. In addition, only organizations with 500 or fewer employees managed to keep their CFCR under 30%.
To put these numbers into perspective, if an enterprise-level organization of 10,000 employees had been targeted with a phishing scam similar to the event’s simulation, 700 would’ve clicked on the initial phishing link, and 308 would’ve compromised sensitive information via the web form.
RESULTS COMPARISON 2022 vs 2021
Data breakdown by industry: which sector fared best?
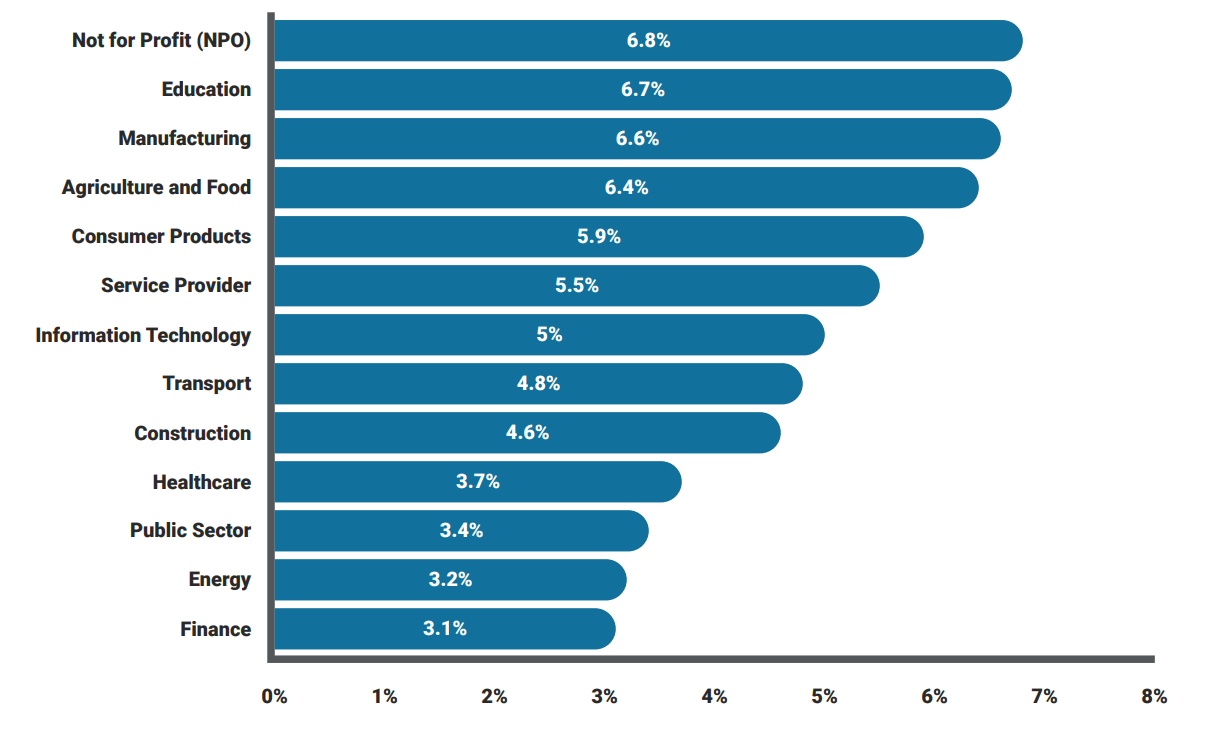
When measuring click rates between organizations based on their industry , it’s important to recognize that no two starting points will be the same. Varying levels of cyber security standards, compliance requirements, and so on mean phishing simulation performance will differ from organization to organization, even if they’re operating in the same milieu. The following sectors posted the highest phishing email click rates:
Not for Profit
Education
Manufacturing
Agriculture and Food
Consumer Products
The best performing sectors regarding click rates were Finance, Energy, and the Public Sector, all posting results under 3.5%
CLICKED LINK BY INDUSTRY (%)
Education also topped the by-sector list when it came to overall credential submission rates, coming in at a shade under 3%. Only Finance and Energy managed to keep their form completion rate under 1%.
COMPLETED FORM BY INDUSTRY (%)
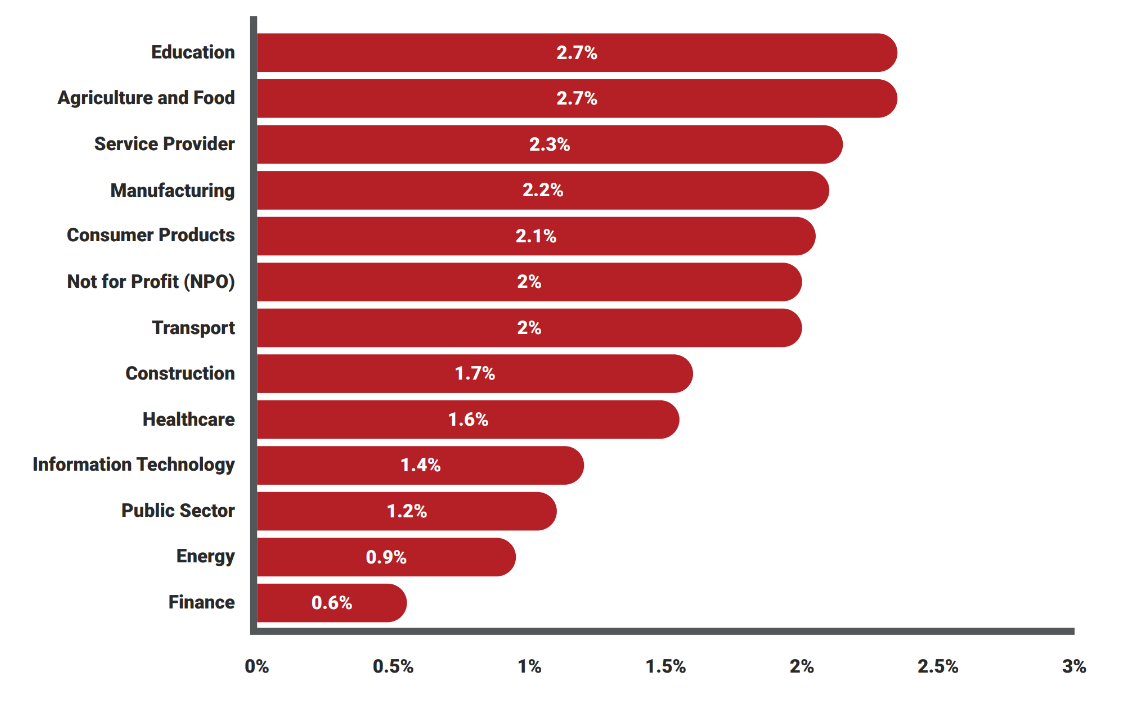
However, as with the tournament’s global results, arguably the biggest sector-based surprise is the organizations who registered the highest CFCR totals. Organizations operating in the Consumer Products space posted a CFCR of nearly 40%, with Agriculture and Food and Transport faring not much better.
Sectors that did perform well were IT, Energy, and Finance, which all had a CFCR of less than 20%.
CLICKERS WHO COMPLETED THE FORM BY INDUSTRY (%)
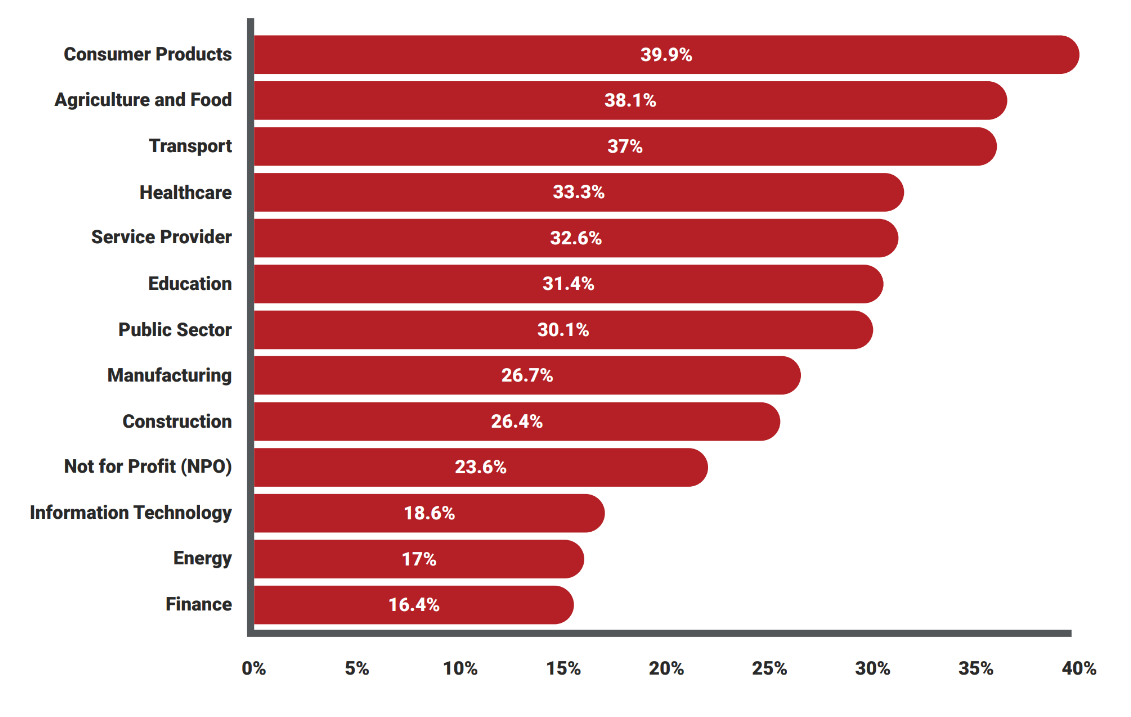
Still, these results highlight how, for specific industries, completing a form via a link is more a part of end users’ day-to-day activities, rendering the phishing simulation more relevant based on their roles. On the other hand, other industries may not encounter this type of threat on even an occasional basis, potentially making the simulated phishing email easier to pinpoint and report.
Data breakdown by number of employees: when does size matter?
In the context of security awareness training, this section’s titular question comes up frequently. In short, do more internal resources—including a budget, staff devoted to related initiatives, and so on– result in lower end-user click rates overall? The answer is far more complex than “yes” and “no.”
The 2022 simulation shows that size of the organization influences click rate and CFCR, but not necessarily in the most obvious ways. In short, large organizations, many of whom typically have access to more cyber security resources than smaller businesses, registered the highest click rate total. The level below enterprise, in the 3000-9999 employee range, finished with the second-highest rate.
CLICKED LINK BY ORGANIZATION SIZE (%)
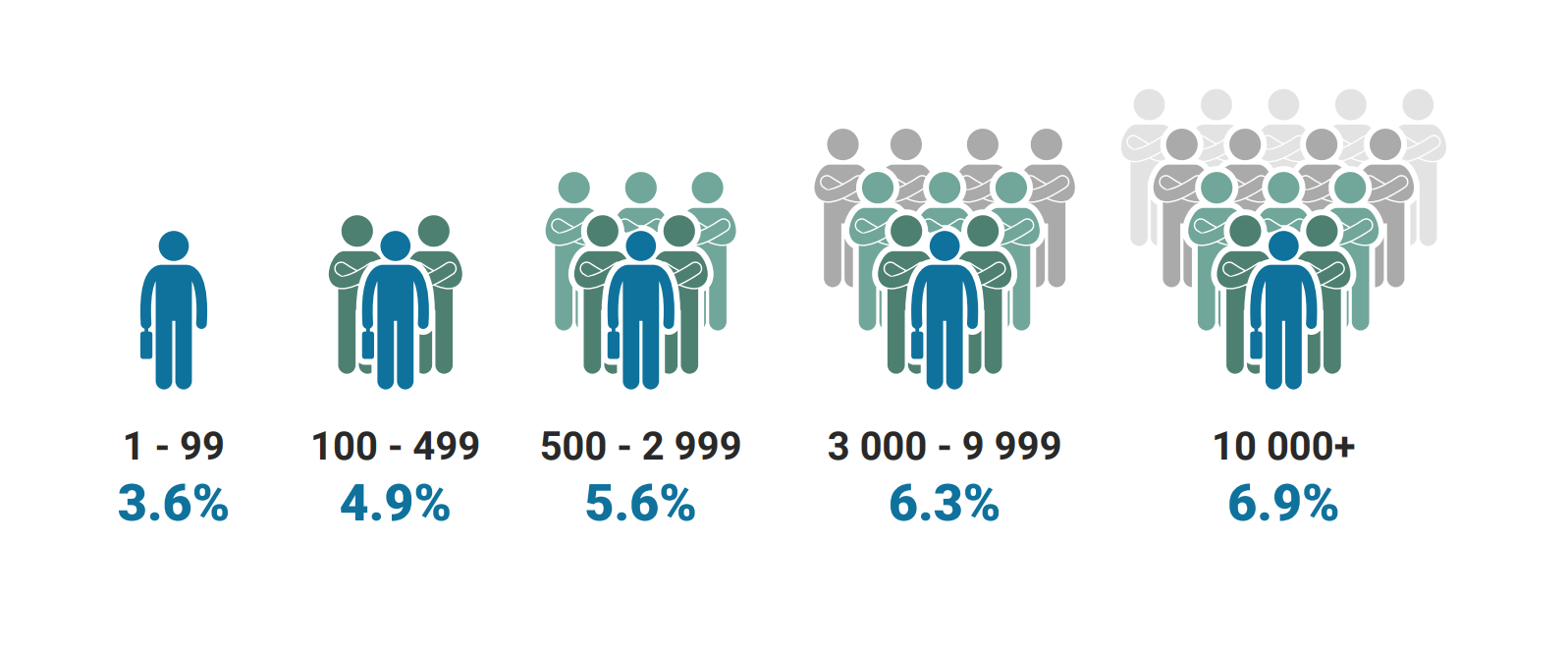
Organizations in the 1-99 employee count range fared the best at under 3.6%. Taking the high end of that range, it works out to about 3 or 4 employees clicking on a phishing email link. Now compare that number to 6.9% from organizations with 10,000 employees or more, which skyrockets that total to 690 end users.
CLICKERS WHO COMPLETED THE FORM BY ORGANIZATION SIZE (%)
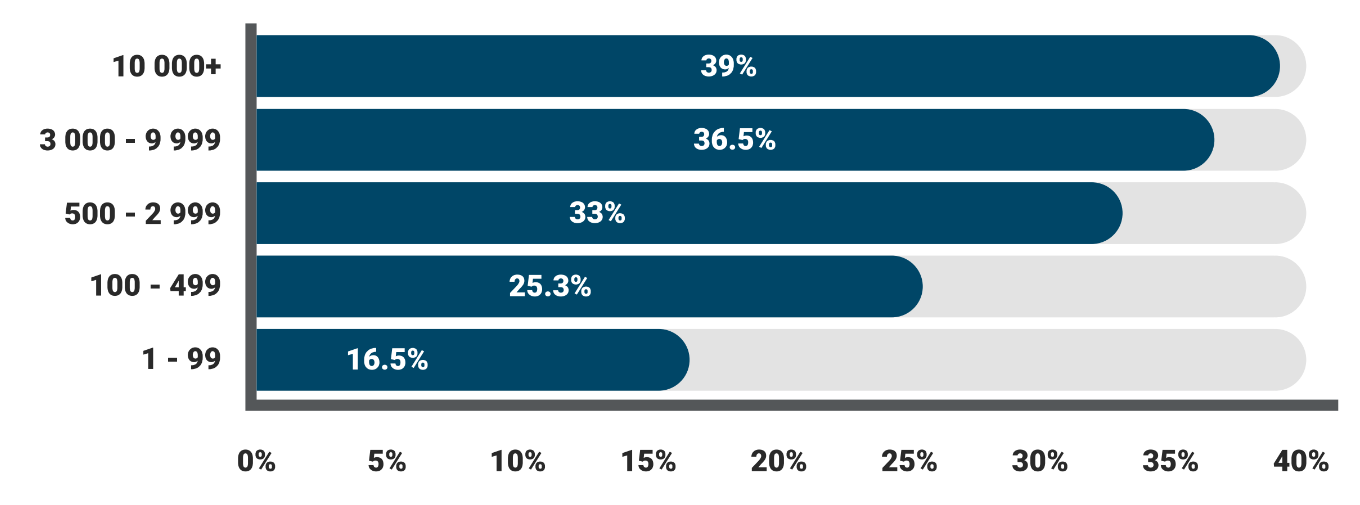
While there wasn’t much to separate the form submission percentages between the organization size segments, the CFCR yielded some eye-opening results. Once again, organizations in the 10,000+ employee count range finished with the highest result at 39%. The 3000-9999 range wasn’t far behind either, with 36.5% of clickers eventually completing the form on the phishing simulation webpage.
These results demonstrate that a bigger employee base doesn’t mean better cyber security practices. A 39% CFCR results for enterprise-level organizations means, of the 690 end users who would’ve clicked on a phishing email link had the simulation been real, 269 of them would’ve compromised their account credentials in the webpage form.
Considering the size and volume of transactions organizations of this ilk handle on a yearly basis, this reality should be more than a little concerning for security leaders.
In a broad sense, an organization’s security awareness training program strategy and individual initiative execution may matter more than its resources. According to participant data, while organizations with 10,000 employees or more rarely missed a security awareness training solution, their overall effectiveness may be lacking.
Larger organizations often have challenges reaching out to all employees with awareness activities and achieving a high participation rate. Large organizations have the added challenge of accounting for and onboarding more employees, especially in a remote-first environment.
Data breakdown by region: does location make a difference?
An organization’s region, as it relates to its operating jurisdiction and where its employee base is located, plays an increasingly critical part in cyber security awareness levels. In the EU, data privacy and compliance regulations like GDPR can influence how an organization collects, stores, and manipulates consumer data, as well as how much news coverage is devoted to significant data breaches.
As distributed workforces become a global norm across many industries, IT departments have an increasingly challenging mission of ensuring all employees can recognize and safeguard against cyber threats. And, though the 2022 GPT results are an improvement over those from 2021, they also highlight the complexity of navigating changing sensibilities.
CLICKED LINK BY REGION (%)
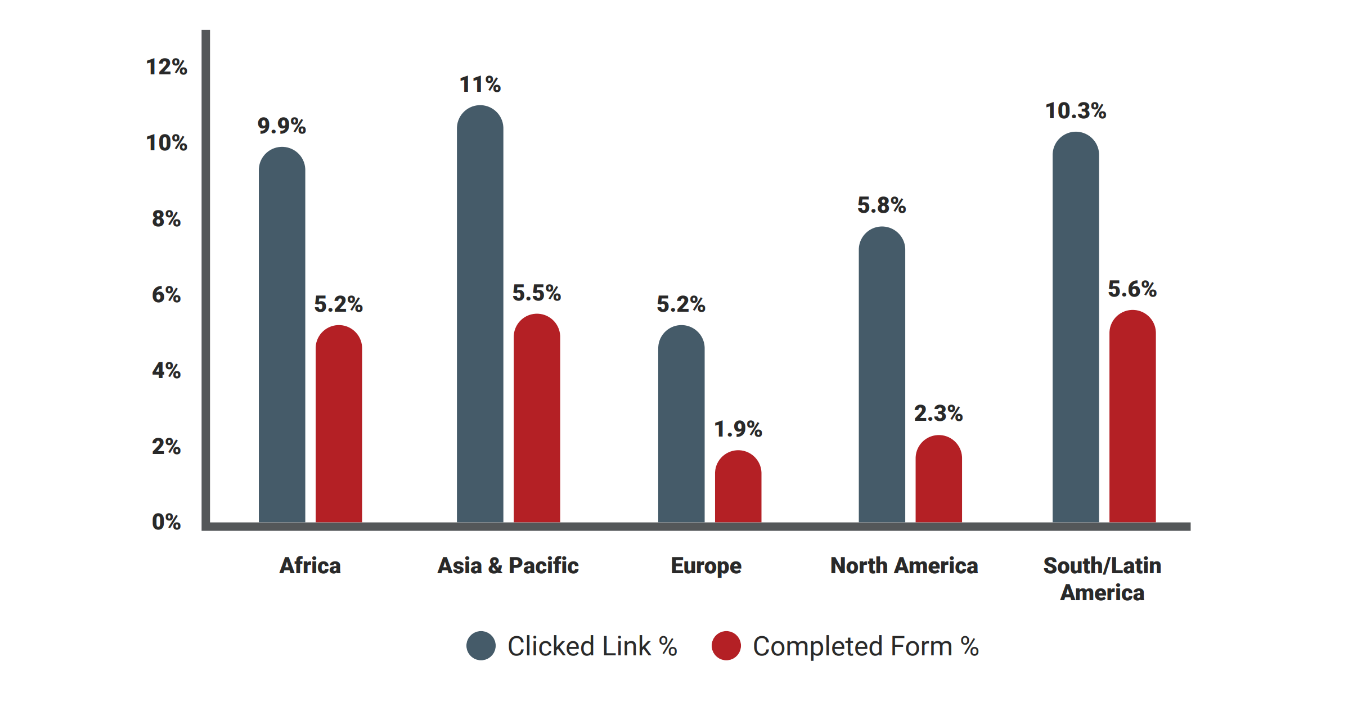
Of the five regions represented by GPT participants, Europe was the top performer, claiming the lowest email link click rate and form completion rates. North America, the top-performing region in 2021, slotted into second place.
Meanwhile, participants from the Asia & Pacific region registered the highest click rate, one of only two regions to see their score balloon to double digits. South/Latin America had the highest form completion rate, narrowly edging out Asia & Pacific participants by 0.1% in this category.
CLICKERS WHO COMPLETED THE FORM BY REGION (%)
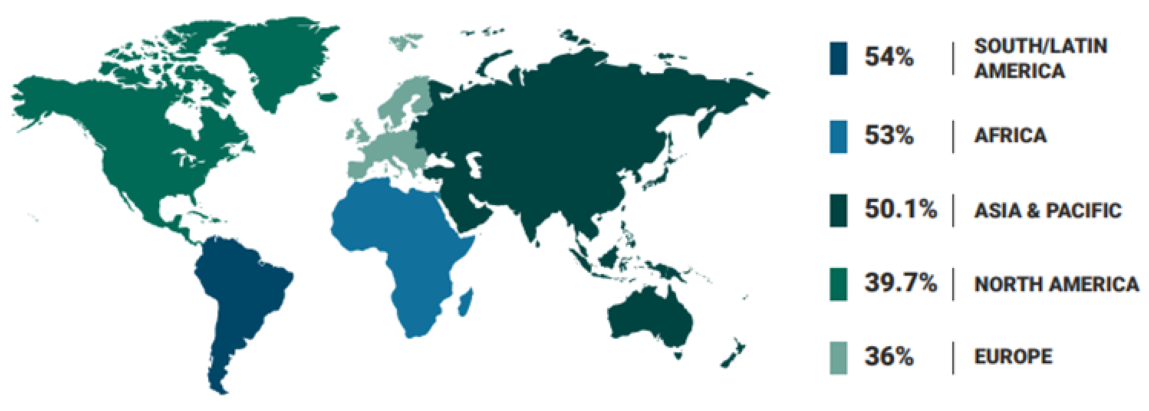
As in previous editions of the GPT, those initial metrics don’t tell the entire story. While Europe-based end users ended up with the lowest CFCR overall, individuals in South/Latin America registered the highest total in this category, followed closely by Africa. The latter region’s result is especially intriguing since it finished middle-of-the-pack for other regional metrics.
The relatively high CFCR can be attributed to the real-world nature of the phishing simulation Terranova Security designed for this year’s event. Phishing threats are constantly evolving to mirror suspicious messages any professional may encounter in their day-to-day activities. Tapping into this familiarity makes it much easier for threats like this one to go undetected.
On top of that, the best security awareness training must include recent data and tactics leveraged by hackers in phishing attacks. If those elements aren’t present, the overall end user experience may not share updated threat information, which, in turn, can weaken the knowledge baseline all employees need to detect and report potential cyber attacks consistently.
How to Launch Powerful Phishing Simulation Training
Importance of targeting behaviors through risk-based training campaigns
These days, security awareness is about more than simply deploying training courses and phishing simulations.
Those components are integral to the process, as they add a dynamic, learning-by-doing dimension to any training program. But it’s only the tip of the iceberg. Strengthening information security demands that organizations build and grow a culture where cyber security best practices are top of mind for all employees.
To get there, security leaders need insights to determine individual risk levels per end user or role profile. Fueling risk assessment with data-driven ratings, like those generated using the Security Culture Index from Terranova Security, facilitates pinpointing high-risk users, driving behavior change, and bolsters a cyber security culture over time.
Phishing simulations and other security awareness initiatives must rely on actionable data to achieve maximum efficacy. Without it, the success of the resulting training campaigns will ultimately wane.
Maximizing results with risk-based phishing training campaigns
With the right data, security leaders must establish a security awareness strategy supported by a proven framework for lasting behavior change. Setting the foundation for a defined end-user learning path ensures your awareness training campaigns target the correct user habits most often leveraged by hackers.
Terranova Security has identified seven common behaviors targeted by cyber threats, based on Microsoft payloads, that every organization should be mindful of:
THREATS
- Attachment Malware
- Link to Malware File
- Link in Attachment
- Drive-By URL
- Credential Harvesting
- Business Email Compromise
BEHAVIORS
- Open Malware Attachment
- Clicking on a Link or Button
- Giving Out UID/PW
- Giving Out Employee PII
- Giving Out Corporate Financial Info
- Giving Out Personal PII
- Giving Out Personal Financial Info
Risk-based Training Example
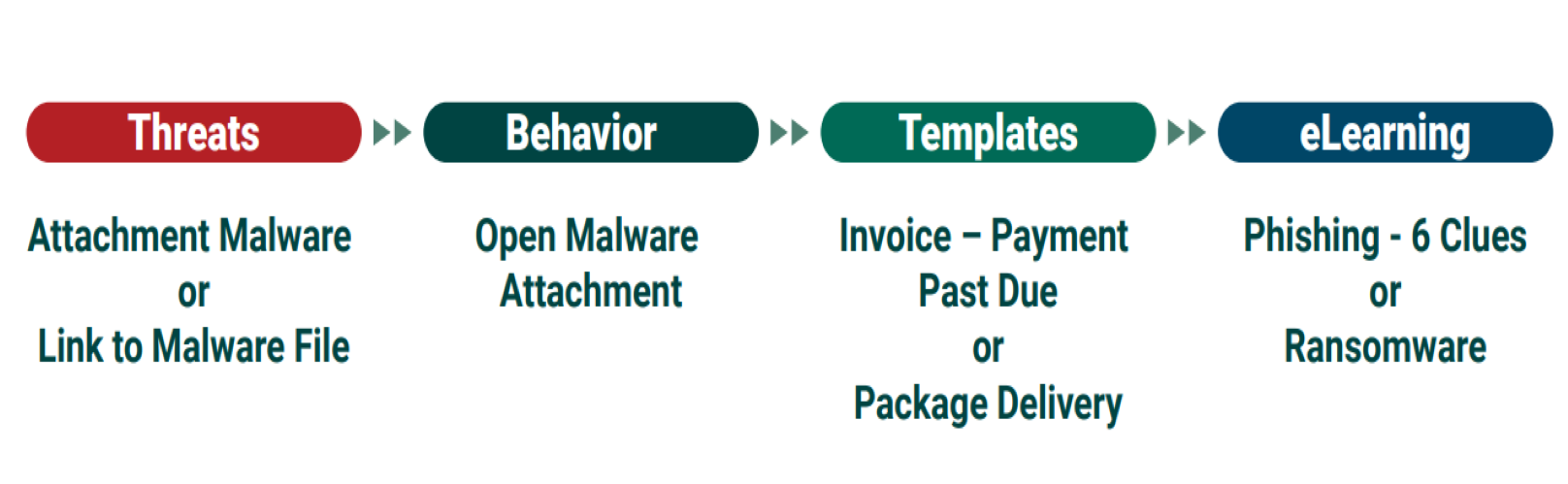
This illustration depicts the link between a given threat and user behavior, which may compromise their sensitive data. In this case, the threat is a malware attachment or link. Based on the behavior(s) you want to counteract, your training modules and phishing simulations must work in tandem to teach employees the proper steps to take when faced with a specific cyber threat scenario.
Once your strategy is set, Terranova Security recommends using communication tools to encourage participation across all business units once your awareness training is ready to launch. Post-launch, start with a general phishing module that establishes vital baseline knowledge across the organization and provides a foundational starting point from which to work.
As scenarios vary in complexity, the phishing simulations you choose to launch will impact the click rate. If your users never click on the phishing simulation email links, the chosen scenarios may not be challenging enough. Quality over quantity is a significant consideration here.
How to launch effective phishing simulations
Taking a proactive, data-based approach to security awareness training and phishing simulations can be easier than many organizations may think. To educate users and change key behaviors cyber criminals can look to exploit, follow these simple guidelines:
- Target the right user behaviors by delving into your existing cyber security data and pinpointing patterns or specific actions that have led to data breaches
- Create phishing simulations that address those weaknesses and leverage up-to-date scenarios that users may encounter in their daily lives
- Collect real-time phishing simulation data to facilitate the assessment, maintenance, and refinement of your security awareness initiatives
- Track and monitor user progress to determine user-specific risk ratings and the overall effectiveness of your security awareness approach
- Deploy just-in-time training modules to give users the instant feedback they need should they fail a phishing simulation
- Utilize customizable training campaigns based on the data you collect to tailor every aspect of the process to your needs and drive goal attainment
- Choose a scalable, inclusive solution with multilingual, accessible training content that makes catering eLearning to a diverse, global employee base seamless
CISO Recommendations for Employees
To avoid falling victim to phishing threats like the one depicted in this report, Terranova Security CISOs recommend employees always keep the following best practices in mind:
Verify an email sender’s domain name.
Analyze the message’s contents and tone.
Never send sensitive information via email.
Avoid clicking on unexpected email links.
Inspect web sites before submitting data.
CISO Recommendations for Security Leaders
To ensure your organization is doing everything it can to build a successful security awareness training campaign, Terranova Security CISOs recommend taking the following steps: